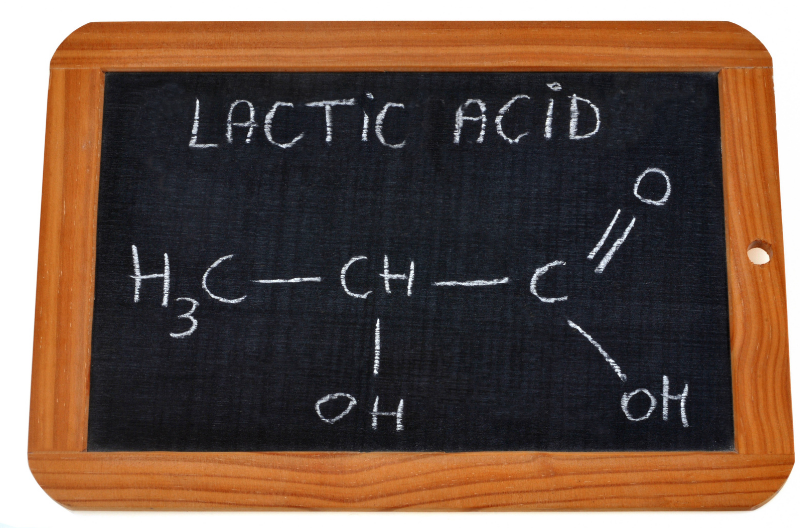
Lactic acid is essential for the healthy functioning of the system. It improves focus while exercising without causing muscular discomfort. Also, it is needed for normal biological function and is not just a result of exercise.
Some medical diseases may lead to the increased lactic acid formation or a decrease in the body’s capacity to remove lactate from circulation. In this guide, we will address the often asked questions regarding what supplement helps reduce lactic acid.
Why does your body produce lactic acid
When we exercise, our bodies utilize a large amount of oxygen to disintegrate glucose into energy. However, during strenuous activity, the need for oxygen arises, making it harder for our bodies to supply the requirement. The lack of oxygen results in the development of lactate in the muscles, which is transformed into energy. This lactate or lactic acid is produced quicker than our bodies can burn when exercising.
Moreover, the lactic acid level returns to usual as soon as you stop exercising. The excess lactic acid is carried through the bloodstream and eliminated via the liver. However, specific individuals are predisposed to lactic acidosis, a condition in which lactic acid accumulates in the circulation. This may cause pain, as well as a burning feeling long after the workout.
Certain medical disorders, including malignancy, kidney dysfunction, sepsis, shock, and vitamin D insufficiency, may also cause lactic acid build-up. Additionally, certain medicines might have a similar impact on the body.
💡 Lactate works faster than glucose for energy
What happens if your lactic acid is high
Lactic Acidosis and Hyperlactatemia may result from high amounts of lactic acid in the blood. Some medical issues might enhance a person’s chances of getting hyperlactatemia and lactic acidosis. Both of these disorders, if left untreated, may result in serious, perhaps deadly consequences.
💡 Athletes produce more lactic acid.
How do you know if you have lactic acid build up
If you have lactic acidosis and experience any of the following symptoms, you may have lactic acid build-up.
- severe weariness or exhaustion
- spasms or discomfort in the muscles
- body weakness
- nonspecific feelings of physical pain
- abdominal discomfort
- diarrhea
- a reduction in appetite
- headache
- a fast heartbeat
💡 Lactate heals the brain after traumatic injuries.
What can you take to reduce lactic acid
High lactic acid accumulation in the muscles was formerly considered to induce muscular pain and weariness after an intense exercise. According to the science-based homepage, lactic acid works as a fuel source for muscular tissue, and effective delivery to muscle cells causes energy to burn.
For muscle healing and decreased discomfort after exercise, you need appropriate nutrition and make sure to avoid activities that promote muscle injury and collapse. Some OTC supplements claim to be lactic acid reduces and stimulates muscle repair. Consult your doctor before using these products.
Protein and Omega-3

Omega-3 fatty acids are necessary nutrients that support the brain, heart, and metabolic processes. Nuts and fish are high in omega-3 fatty acids. These meals are also high in protein, necessary for muscle development, restoration, and rehabilitation. According to a 2014 research published in the Journal of Sports Science & Medicine, these supplements aid in muscle rehabilitation after strenuous activity. However, the dose varies, like with other supplements, and should be reviewed with your physician before usage.
Magnesium

Magnesium is a nutritional mineral required for metabolic activities, such as energy generation and oxygen use. Based on HealthLine, magnesium in supplementation may effectively lower lactic acid accumulation after strenuous exercise. Magnesium is found in nuts, leafy green vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. Moreover, magnesium supplements come in various forms, but they are usually combined with buffering substances to avoid an excess of pure magnesium in circulation. Keep in mind that adults should consume 320 to 410 mg of magnesium per day. But before using magnesium supplements, see your doctor first.
Creatine

Creatine is a naturally occurring amino acid that may also be obtained from protein-rich meals. Throughout metabolism, creatine is converted to phosphate and deposited in your muscles. It gives energy to muscle cells, which is especially important during activity.
If more creatine is available in your muscles before activity, it may function as a lactic acid buffer, and it can help in muscle repair when eaten after exercise. Powders, liquids, pills, and beverages are available as supplements. Check with your doctor before taking creatine since having too much generates a byproduct that is toxic to the kidneys and liver.
💡 Considered to boost strength, increase lean muscle mass, and aid in muscle recovery after exercise. This muscle surge may assist athletes in achieving bursts of speed and energy, particularly during brief bouts of high-intensity activity like weight lifting or running.
How long does it take for lactic acid to go away

Lactic acid build-up lasts between three to five days typically. The discomfort, which may vary from minor to severe, generally manifests one or two days following the workout. This kind of muscular pain must not be mistaken with any other type of pain you can feel when exercising, such as the acute, abrupt, and intense pain of an injury, including muscle sprains.
Thanks for reading! Share your thoughts and comments, and don’t forget to read our latest blog, 11 Best Supplements For Baseball Player!